Scientists Make Epic Antimatter Breakthrough! 🚀
Get ready, science enthusiasts! A team of Chinese and international physicists has just dropped some major news in the world of physics. They've observed a brand-new antimatter hypernucleus called anti-hyperhydrogen-4—and it's the heaviest one spotted so far! 🤯
The discovery was led by the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and was recently published in the prestigious journal Nature. This is a huge leap forward in our understanding of antimatter and could help answer some of the universe's biggest mysteries.
So, what's the big deal about antimatter? Well, according to current physics theories, when the universe was born, there were equal amounts of matter and antimatter. But something caused a tiny imbalance, leaving us with more matter—which makes up everything we see around us today. Scientists are trying to figure out why that happened.
"What caused the difference in quantities of matter and antimatter in the universe? To answer this question, an important approach is to create new antimatter in the laboratory and study its properties," says Qiu Hao, a researcher from IMP.
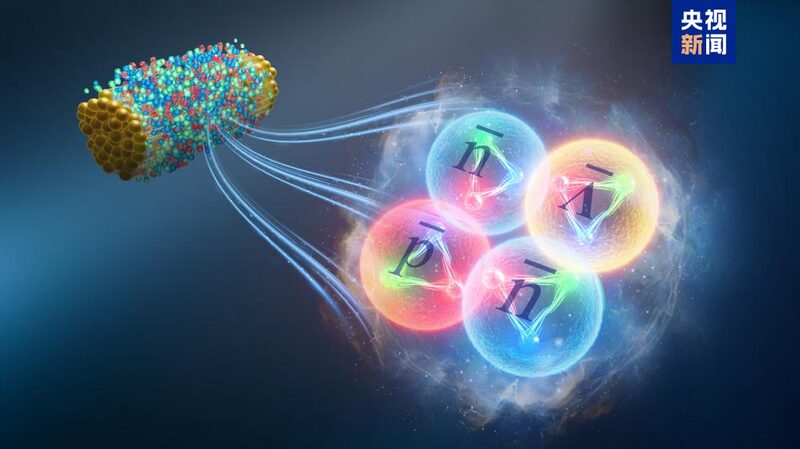
But creating antimatter isn't easy. In today's matter-dominated world, antimatter is super rare because it annihilates when it meets matter. Since 1928, only six types of antimatter nuclei have been discovered. That's why finding anti-hyperhydrogen-4 is such a big deal!
The team produced this new antimatter at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) in the United States. Imagine particles zooming at near light speed and smashing into each other—that's what RHIC does. It creates tiny fireballs hotter than the sun, where matter and antimatter are formed.
"After analyzing data from about 6.6 billion collision events, we reconstructed anti-hyperhydrogen-4 from its decay products," explains Wu Junlin, a PhD student at IMP. Talk about patience and dedication! 💪
The researchers found that the lifetime of anti-hyperhydrogen-4 is similar to its matter counterpart, further confirming that matter and antimatter are symmetrical in their properties. This brings us one step closer to understanding why our universe is made of matter and what happened to all the antimatter.
Who knows? Maybe this discovery will inspire the next generation of physicists among us! 🌌✨
Reference(s):
Breakthrough: China-led team makes new discovery in antimatter
cgtn.com